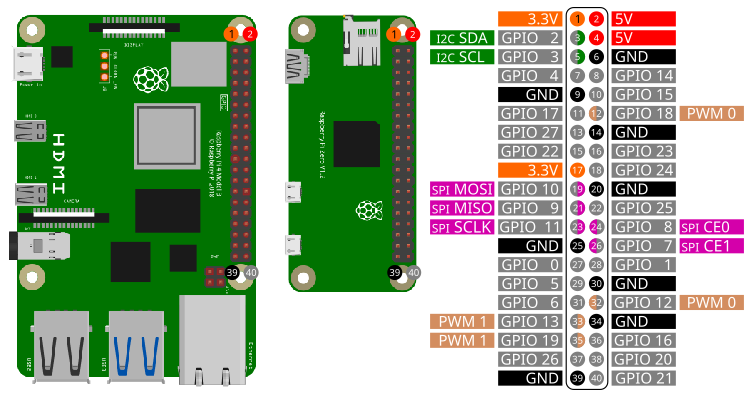

Before start coding you need to setup I2C on the Raspberry Pi. Please following these instructions.

| Pin | Function |
|---|---|
| 2 | SDA |
| 3 | SCL |
Access the basic I2C command with the library i2c:
import i2cid = Open(address)
id = Open(address, interface)Open a connected I2C device with address address on I2C
interface interface. interface is an optional
parameter. Several devices can be opened. id will be used
to identify the device.
address
interface
/dev/i2c-1id
Example:
id = open(0x55)
id = open(0x55, "/dev/i2c-1")Close(id)When closing a SmallBASIC program, I2C access will be automatically
closed. If you want to manually close I2C access for the device with
device id id, use this function.
id
Write(id, dataByte)
Write(id, dataArray)Send one byte dataByte or an 1d array
dataArray of bytes to the devices with device id
id.
id
dataByte
dataArray
Example:
Write(id, 0x20)
Write(id, [0x20, 0x21, 0xA3])WriteReg(id, reg, dataByte)
WriteReg(id, reg, dataArray)Send one byte dataByte or an 1d array
dataBytes of bytes to the devices with device id
id.
id
reg
dataByte
dataArray
Example:
WriteReg(id, 0x05, 0x20)
WriteReg(id, 0x05, [0x20, 0x21, 0xA3])res = Read(id)
res = Read(id, bytes)Read number of bytes bytes from the device with device
id id. bytes is an optional parameter.
id
bytes
1res
res is an 1d array.res = Read(id, reg)
res = Read(id, reg, bytes)Read number of bytes bytes from the register
reg of the device with device id id.
bytes is an optional parameter.
id
reg
bytes
1res
res is an 1d array.Example:
res = ReadReg(id, 0x05) ' Read one byte from register 0x05
res = ReadReg(id, 0x05, 5) ' Read five bytes from register 0x05res = SmbusReadByte(id, reg)Read one byte from the register reg of the SMBus device
with device id id.
id
reg
res
Example:
res = SmbusReadByte(id, 0x05) ' Read one byte from register 0x05res = SmbusReadWord(id, reg)Read one word (2 bytes) from the register reg of the
SMBus device with device id id.
id
reg
res
Example:
res = SmbusReadWord(id, 0x05) ' Read one byte from register 0x05SmbusWriteByte(id, reg, data)Send one byte to the register reg of the SMBus device
with device id id.
id
reg
data
Example:
SmbusWriteByte(id, 0x05, 0xA2) ' Write 0xA2 to register 0x05SmbusWriteWord(id, reg, data)Send one word (2 bytes) to the register reg of the SMBus
device with device id id.
id
reg
data
Example:
SmbusWriteWord(id, 0x05, 0xA202) ' Write 0xA202 to register 0x05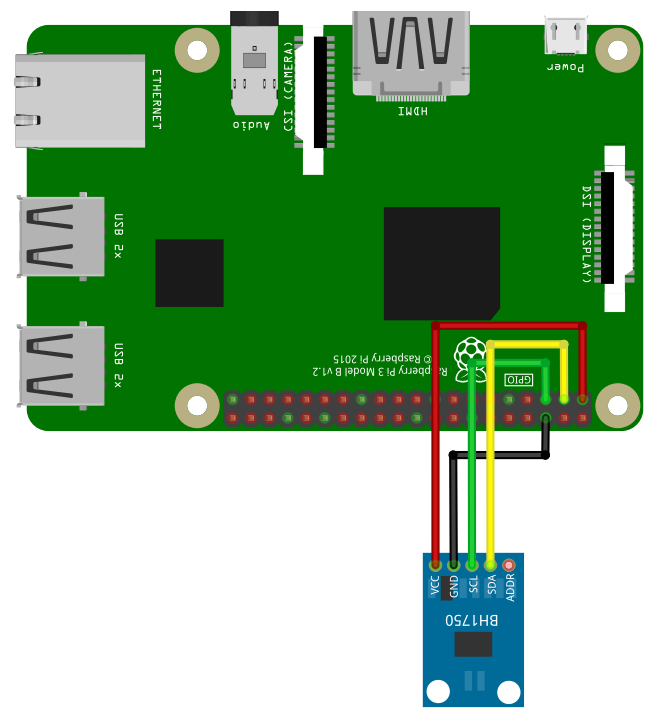
Please be careful, the sensors are usually driven with 3.3V. The sensor from Adafruit can be driven with 3.3V or 5V. If you don’t connect the address pin, then the sensor will use address 0x23.
import i2c
Print "Connect to BH1750"
sensor = i2c.Open(0x23, "/dev/i2c-1")
' Power down
i2c.write(sensor, 0x00)
' Power on
i2c.write(sensor, 0x01)
delay(1000)
' Read one time with low resolution
d = i2c.ReadReg(sensor, 0x23, 2)
ValueLowRes = ((d[0] lshift 8) BOR d[1]) / 1.2
delay(1000)
' Read one time with high resolution
d = i2c.ReadReg(sensor, 0x20, 2)
ValueHighRes = ((d[0] lshift 8) BOR d[1]) / 1.2
print "Low resolution : " + ValueLowRes + " lx"
print "High resolution: " + valueHighRes + " lx"import i2c
Print "Access PiSugar 3 Plus"
PiSugar = i2c.Open(0x57, "/dev/i2c-1")
ChargeStatus = i2c.SmbusReadByte(PiSugar, 0x2A)
print ChargeStatus; "%"
VoltageHigh = i2c.SmbusReadByte(PiSugar, 0x22)
VoltageLow = i2c.SmbusReadByte(PiSugar, 0x23)
Voltage = (VoltageHigh lshift 8) + VoltageLow
print Voltage; "mV"
IsPowerConnected = i2c.SmbusReadByte(PiSugar, 0x02) rshift 7
print "USB Power connected: "; IsPowerConnected
print "Seconds of RTC: "; i2c.SmbusReadByte(PiSugar, 0x37)